3,000-Year-Old Castle Built by Mysterious Civilization Found at The Bottom of a Lake in Turkey
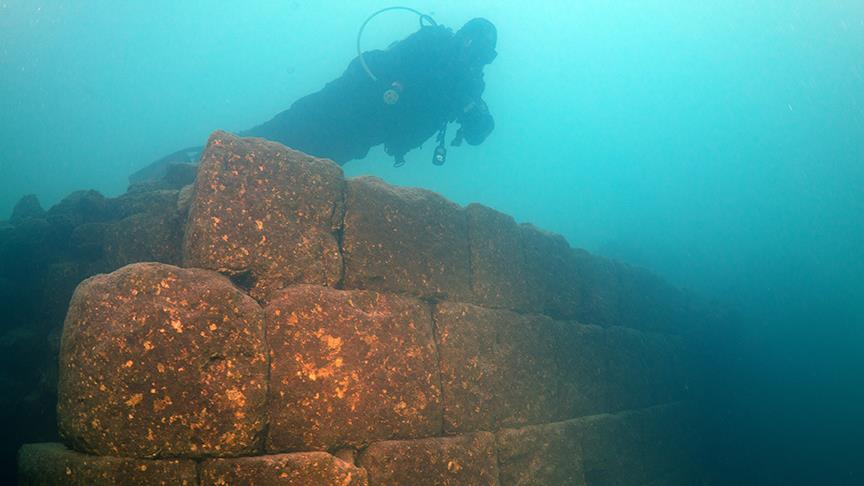

A team of Turkish archaeologists has discovered the remains of what is believed to be a 3,000-year-old castle from the Armenian kingdom of Urartu (Ararat) submerged underwater in Lake Van.
The underwater excavations were led by Van Yüzüncü Yıl University and the governorship of Turkey’s eastern Bitlis Province. The castle is said to belong to the Iron Age Armenian civilization also known as the Kingdom of Van, Urartu, Ararat, and Armenia.
The lake itself is believed to have been formed by a crater caused by a volcanic eruption of Mount Nemrut near the province of Van. The current water level of the reservoir is about 150 meters higher than it was during the Iron Age.
“Civilizations living around the lake set up large villages and settlements while the water level of the lake was low, but they had to leave the area after it increased again,”
said Tahsin Ceylan, one of the researchers of the newspaper.
The researchers are expecting to conduct further excavations to reveal the full scale of this discovery. The discovery is expected to attract tourism.
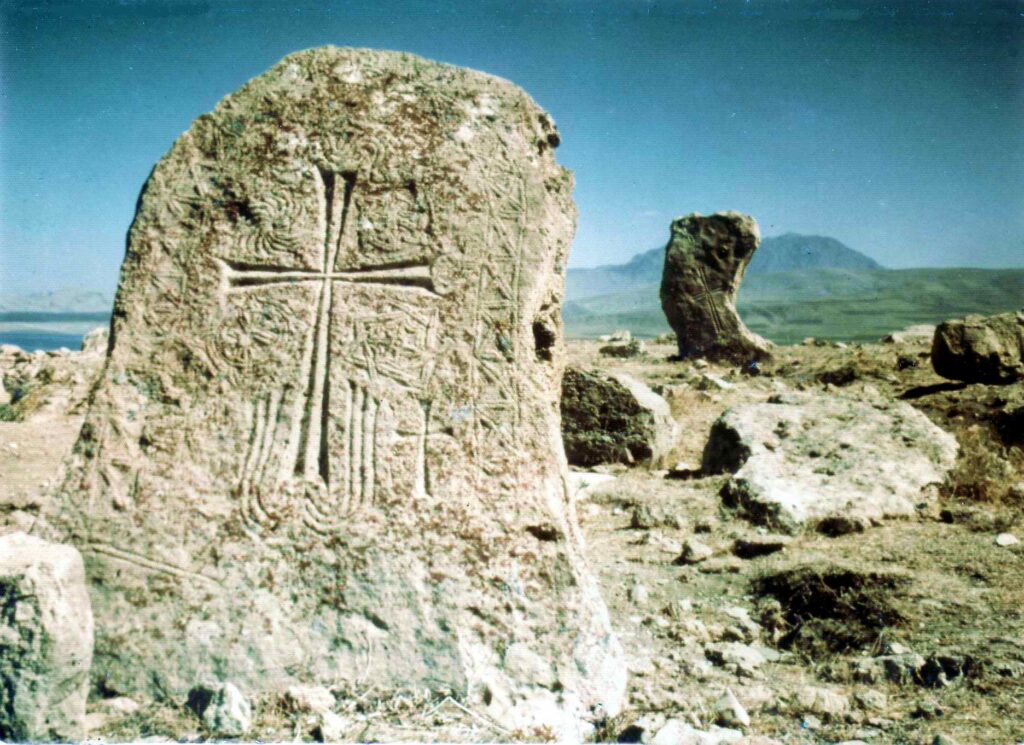
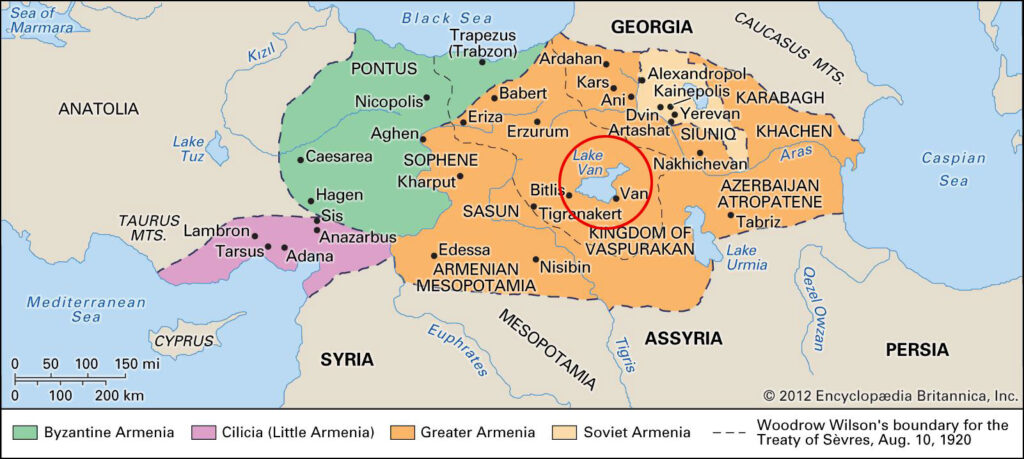
Although now within the borders of the Republic of Turkey, the Lake, and town of Van is the very heartland of Armenian civilization since times immemorial. In fact, so much so, that it is considered the very place where Armenian ethnic identity was first born. According to the records of the 5th-century Armenian historian Movses of Khorene, Hayk (the legendary founder of the Armenian nation) settled near Lake Van in 2492 BC where he first founded the village of Haykashen and build there the mighty fortress of Haykaberd.
At the very shores of Lake, Van Hayk assembled his army and told them that they must defeat the Babylonian tyrant king Bel who had marched against him and his people, or die trying to do so, rather than become his slaves. At Dyutsaznamart (meaning: “Battle of Giants”) near Lake Van, Hayk finally defeated Bel. Hereafter Hayk named the region where the battle took place after his own name and the site of the battle Hayots Dzor (meaning: “Valley of the Armenians”). Thus the Armenian nation and its first free kingdom were born on the very shores of Lake Van after which the Armenians call themselves ‘Hay’ and their country – ‘Hayk’ or ‘Hayastan’, in honor of the legendary founder Hayk.
The ancient Hittite inscriptions deciphered in the 1920s by the Swiss scholar Emil Forrer testify to the existence of a mountain country called ‘Hayasa’ and its vessel lying around Lake Van. The Annals of Mursili (14th century BC) describes the campaigns of Mursili against Hayasa:
And when I arrived in Tiggaramma, the chief cup-bearer Nuvanza and all the noblemen came to meet me at Tiggaramma. I should have marched to Hayasa still, but the chiefs said to me, ‘The season is now far advanced, Sire, Lord! Do not go to Hayasa.’ And I did not go to Hayasa.
It was exactly the works of Movses of Khorene that led to the initial discovery of the Armenian kingdom of Van (Urartu). The existence of this kingdom was unknown to science until the year 1823 when a French scholar, J. Saint-Martin, chanced upon a passage in the ‘History of Armenia’ by Movses of Khorene who had recorded the kingdom in great detail. Inspired by these writings Jean Saint-Martin sent a team to the described location and discovered a kingdom completely unknown to Western academia at the time.
Khorenatsi had described the ancient settlements in Van and attributed them to one of the descendants of Hayk; Ara the Beautiful son of Aram. His description exactly matched, the later discovered, Assyrian clay tablet attributing the foundation of the kingdom to the first king of Urartu; King Aram (c. 860 – 843 BC).
“Urartian history is part of Armenian history, in the same sense that the history of the ancient Britons is part of English history, and that of the Gauls is part of French history. Armenians can legitimately claim, through Urartu, an historical continuity of some 4000 years; their history is among those of the most ancient peoples in the world.”
– Mack Chahin, The Kingdom of Armenia, A History, 1987, revised in 2001
The lake was the center of the Armenian kingdom of Ararat from about 1000 BC, afterward of the Satrapy of Armenia, Kingdom of Greater Armenia, and the Armenian Kingdom of Vaspurakan. Along with Lake Sevan in today’s Armenia and Lake Urmia in today’s Iran, Lake Van was one of the three great lakes of the Armenian Kingdom, referred to as the Seas of Armenia. Its name “Van” is one of the ancient Armenian words for “town” which is still reflected in many Armenian toponyms such as Nakhichevan (meaning: “place/town of descend”), Stepananvan (meaning: “town of Stepan”), Vanadzor (meaning: “valley of Van” ), Sevan, and even the capitol city of Armenia; Yerevan.
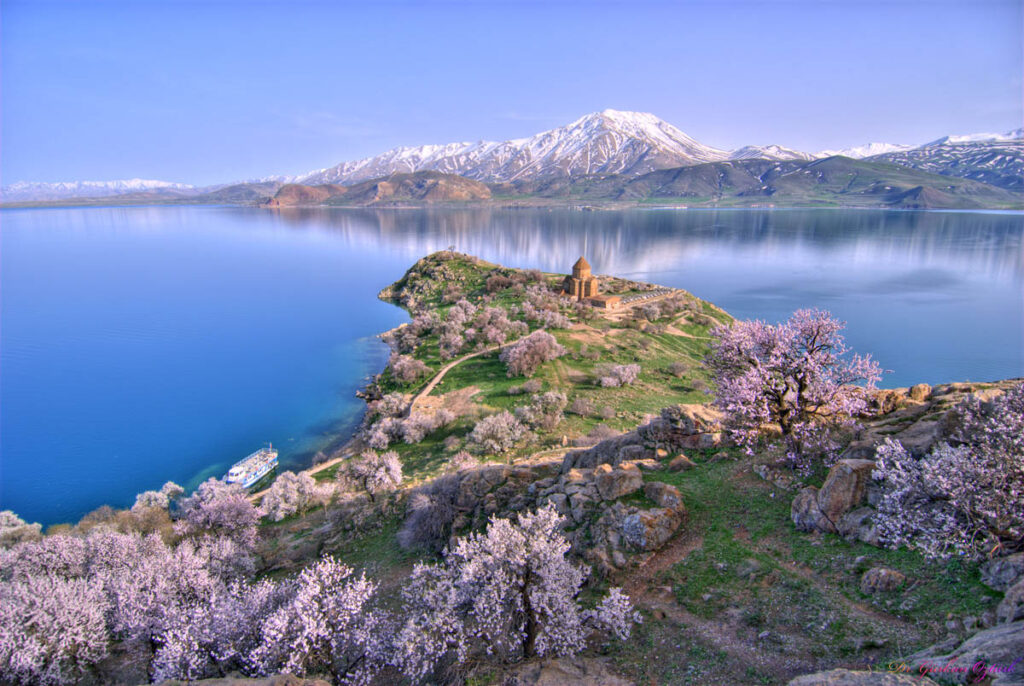
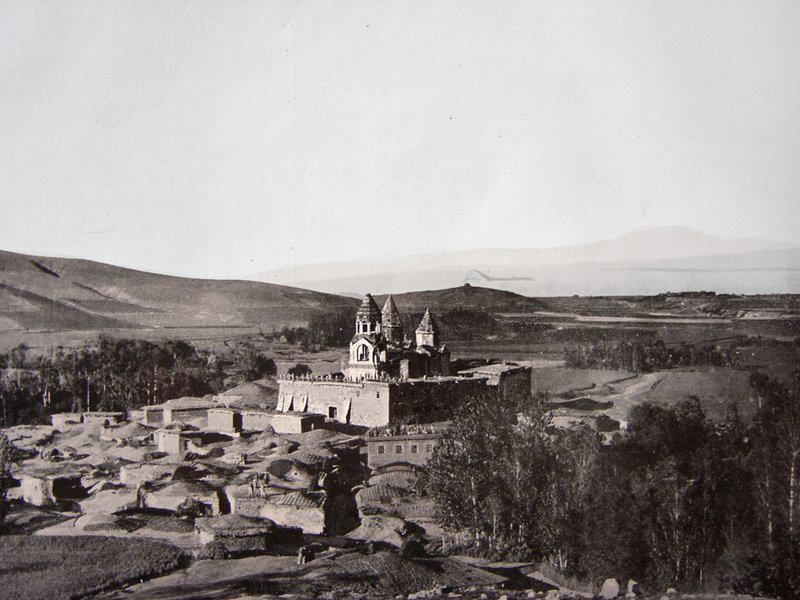
Lake Van and its adjacent town also named Van is today part of Turkey, however, its historic Armenian traces are still visible. At the very center of this lake, there is an island called Akhtamar that still holds a thousand-year-old Armenian church; the Cathedral of the Holy Cross.
Armenians lived in Van up until the early 20th century when Armenians were prosecuted by the Ottoman Turks during the Armenian Genocide. One of the last stands of the Armenian people known as the Resistance of Van, where over 55,000 Armenian civilians were massacred by Ottoman militias and bandits, was extensively discussed in newspapers of that time around the world.
The resistance occupies a significant place in Armenian national identity because it symbolizes the Armenians’ will to resist annihilation at the very heartland of the Armenian people.


